Graduate Degree Requirements
Degree requirements for the Ph.D. in Earth and Environmental Sciences:
A minimum of 45 credits is required for the DEES Ph.D. degree. Students must complete the 45- credit requirement by the Spring semester of their 4th year.
Students develop their overall course plans with guidance from their Advisory Committee. Graduate level courses from other Columbia departments, and graduate level courses taken at other institutions for which Transfer Credit has been awarded, can count for the student’s coursework upon recommendation of the Ph.D. Student’s Advisory Committee. At least half of the student's total coursework will consist of courses taught within DEES, cross-listed within DEES or taught by DEES professors.
The Breadth Requirement:
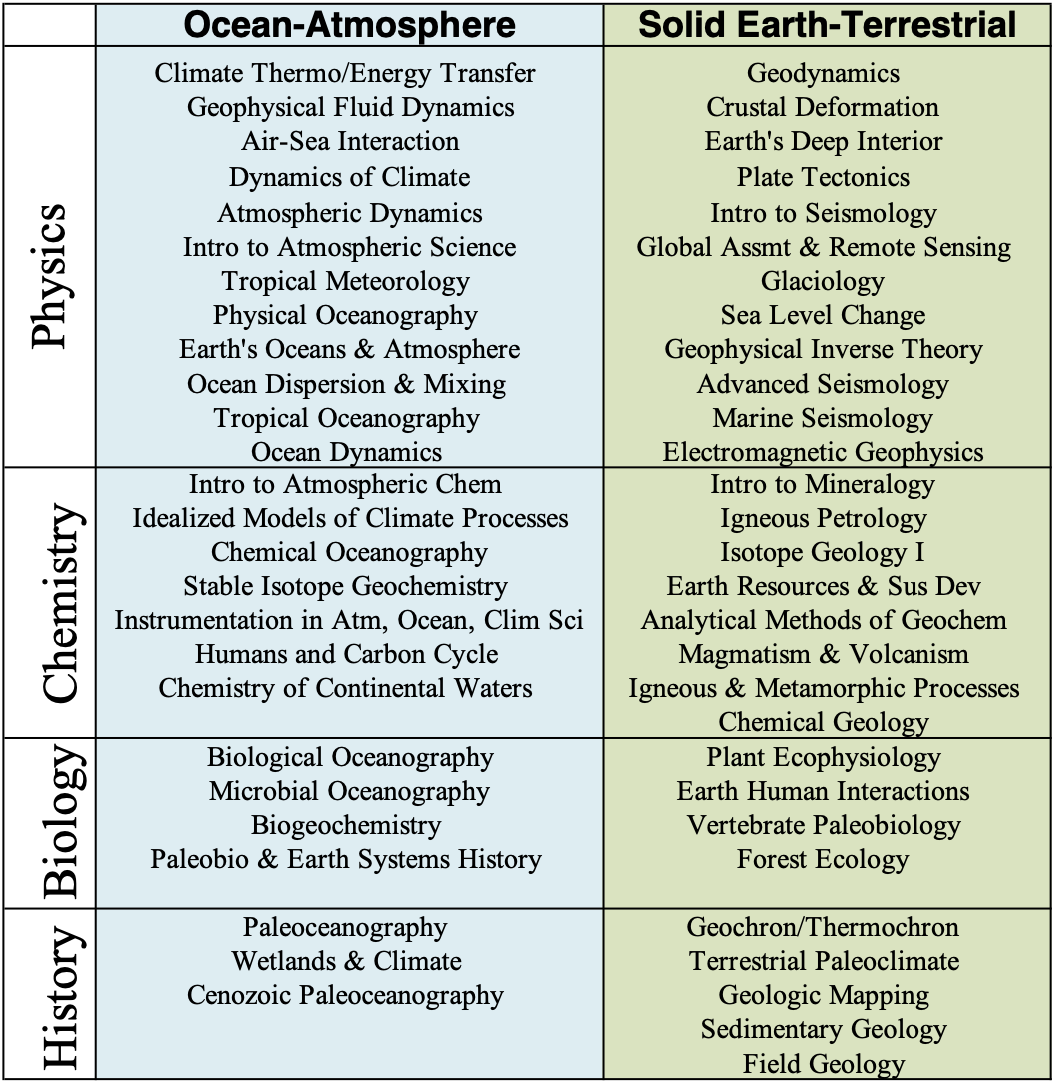
PhD students should obtain mastery and knowledge in their specialized field while developing breadth across Earth and Environmental Science. Breadth puts PhD research in context and is an advantage when communicating to employers, collaborators, future students, funders and the public. Breadth is also a hallmark of DEES and Lamont, known for its fundamental discoveries into the way Earth works - in both her Solid Earth/Terrestrial and Ocean/Atmosphere realms.
A student’s Breadth Requirement is fulfilled when 12 credits (at least 4 courses) are completed within four different breadth areas within the matrix (Physics, Chemistry, Biology, History) x (Ocean-Atmosphere, Solid-Earth-Terrestrial). Two of the breadth courses must be within the Ocean-Atmosphere offerings, and two in the Solid-Earth-Terrestrial offerings. The attached grid reflects current breadth courses; the grid may evolve to reflect new course offerings (providing students new breadth options) and courses no longer taught (which will be grandfathered for breadth credit). All courses used to satisfy the Breadth Requirements must be taken for a letter grade.
The Qualifying Exam
The Qualifying Exam will be administered in the spring of the student’s second year in the Ph.D. program.
The Qualifying Exam consists of a written Qualifying Paper and an oral examination of the Qualifying Paper. The student will be evaluated on their ability and preparedness to conduct Ph.D. level research and demonstrate commensurate academic knowledge of his/her specialties.
The Dissertation Proposal
Students complete the Dissertation Proposal in the spring semester of their
3rd year.
The purpose of the Dissertation Proposal is to formally review the student’s proposed research at
an early enough stage so that comments/guidance can be given to optimize the student’s
research efforts. It should present the Ph.D. dissertation topic, background, goals, outline of any
research completed to date and future research plans, including specific approaches to be
followed and an approximate time table for completing the various stages of the proposed
research.
The Dissertation Defense
Students typically defend their dissertation in the spring or summer of their 5th year.
The Dissertation Defense and deposit of the final dissertation document are the final steps of the Ph.D. program.
The GSAS Dissertation Toolkit is a helpful resource the outlines the details of the dissertation process.
The GSAS Instructional Requirement requires that all Ph.D. Students in the Arts and Sciences assist in the teaching of courses for a total of 2 semesters.
The Teaching Assistant (TA) opportunity provides valuable career experience in teaching, organizing course material, course planning and teacher/student relationships. It also helps students to review material from their own coursework. For more information on the value of being a TA, see the GSAS Student Guide.